+86 137 0938 2367
+86 137 0938 2367
Jun. 09, 2023
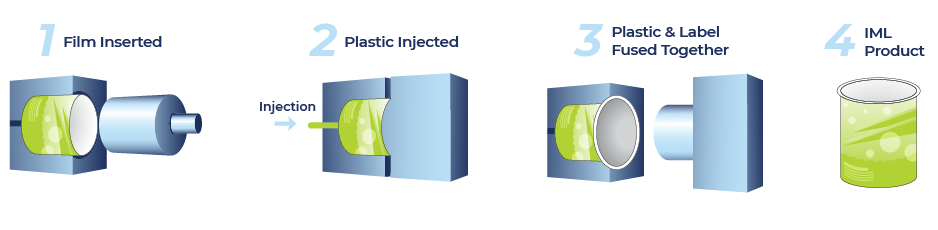
In-mold labeling (IML) is a labeling method in which a pre-printed decorative film is placed into a mold before the plastic container is shaped into that mold. Plastic pellets or resin are heated and placed into the mold where it merges with the label to create a single product. Result: label and packaging become one.
In-mold labeling primarily provides plastic products with high quality and colorful labels. IML is cost-effective and enhances the quality of plastic molded products.
In this article, I will help you to fully understand everything about in-mold labeling.
There are several types of in-mold labeling (IML) processes commonly used in different industries. Here are some of the main types:
Injection molding is the most popular in-mold labeling method, the design label is placed into the mold before fusing together with the container. After the plastic pellets are heated, the resin is injected into the mold where it seamlessly combines with the label.
Blow molding is the second popular in-molding labeling method. This process involves heating plastic material and stretching it into a tube. The plastic tube is placed into a mold. Air is then blown into the plastic tube. This makes the plastic tube to fill the mold cavity. The plastic tube takes the shape or form of the mold.
Just like in-mold injection, the label for decoration is first fixed into the cavity wall of the mold. As the molded plastic cools, it fuses with the label inside the mold cavity. The fusion is made possible because the glue on the label’s surface is activated by the heat from the heated plastic. The blow molding in-mold decoration process results in high durable labeled plastic products.
This process is mostly used for manufacturing hollow plastic parts. This process was used to produce glass bottles. Today, this method is used for producing plastic bottles. This manufacturing process is used to produce liquid containers like containers for shampoos, dishwashing detergents, liquid soap, ketchup, sauces, etc.
Blow molding in-mold labeling can be classified into three main types. They are extrusion blow molding, injection blow molding, and injection stretch blow molding.
Thermoforming IML is used in applications where thin plastic sheets are heated and formed into various shapes, such as trays or packaging containers. In this process, the label is placed on the mold, and the heated plastic sheet is pressed against the label, causing it to adhere to the formed product.

Product labels play a crucial role in the success of plastic products, and in-mold labeling (IML) provides significant benefits in this regard. High-quality labels add value to products by enhancing their appearance and durability.
The design of a plastic product holds the power to attract and entice potential buyers. Studies in modern psychology have shown that people primarily make purchasing decisions based on their emotions. The way individuals feel about a product is often influenced by its visual appeal. If a label is of high quality and visually appealing, it evokes positive emotions and influences the perception of the product's quality.
In this context, a well-designed label has the potential to drive customers to purchase a product, even before considering its functional benefits. Conversely, a high-quality product with an unattractive appearance may struggle in the market. On the other hand, a low-quality product with an attractive label or design can still attract a significant number of buyers.
Manufacturers must therefore dedicate considerable attention to the design and appearance of their products. In-mold labeling offers a cost-effective process for brands to obtain high-quality designs for their products, resulting in improved aesthetics, increased durability, and ultimately, greater customer appeal.
The main principle of in-mold labeling is to coat a product with a layer of label or design.
The in-mold labeling process begins with selecting a unique material for labeling. Some of the materials used as labels include paper, polypropylene, and polystyrene. A material similar to the molded part can also be used as a label.
A cavitated material can be also used as a label. A cavitated label material is a spongy layer that is bonded between two thin solid layers. A laminated film is used as a label when high resistance to wear is of great importance.
The selected label is directed into an open mold. It is firmly placed into the mold cavity by either a clamp, vacuum, compressed air, or static electricity.
The selected plastic material is melted and injected into the mold. The injected plastic material binds with the label after cooling to form a single product. This produces a beautiful design on the molded product.

In-mold labeling provides high resolution colors and images for labels. IML is compatible with a wide range of colors and can be displayed on both sides of the package. In-mold labeling is a powerful platform for enhancing graphic effects, enabling business owners the flexibility to respond to creative design ideas using flat, curved, or 3D-formed graphics.
The label is fused to the plastic giving the in-mold container a clean, smooth, integrated and unlabeled look as opposed to post-mold labeling (PML). This label remains intact throughout its life and is highly tamper-proof unless the container is cut open.
The water resistance of in-mold labeling makes it a reliable labeling option that can withstand both humid environments and extreme temperature fluctuations (freezing / cooling conditions). In contrast to pressure sensitive labeling, IML is a permanent design method with excellent impact and scratch resistance because it fuses permanently to the container.
A container with in-mold labeling has the potential to be impervious to abrasion and chemicals depending on the hard coatings used to generate the manufactured goods.
Traditional methods of pressure sensitive labeling require adhesives that are not accepted by every recycling plant. Because both the container and the label are combined without the exterior glue, plastic products with IML can be eco-friendly and fully recyclable depending on the type of plastic resin used to manufacture the product.
Since in-mold labeling containers are completely recyclable, they are eligible to become PCR products which can help decrease carbon footprints and leave a positive impact on the environment.
For mass production, in-mold labeling containers take less time to manufacture because it is produced and decorated in one step to form a single product. In comparison to PML, in-mold labeling is typically more cost-efficient because it is without the expense of time, labor and floor space; IML also reduces inventory like post-mold paper labels and adhesives.
Higher Initial Investment: Implementing in-mold labeling may require initial investment in specialized equipment and molds that are specifically designed for IML. This can increase the upfront costs compared to traditional labeling methods.
Longer Lead Times: The process of in-mold labeling typically involves additional steps and considerations, such as label preparation and precise placement. This can lead to longer lead times for production compared to simpler labeling techniques.
Limited Label Variation: In-mold labeling often involves using pre-printed labels that are applied to products during the molding process. This can limit the ability to make immediate changes or variations in the label design without incurring additional costs for creating new molds or labels.
Higher Reject Rates: In some cases, the integration of the label with the product during the molding process may lead to higher reject rates. If there are issues with label placement or adhesion, it can result in imperfect products that do not meet quality standards.
In-mold labeling (IML) is widely used in various industries for different applications. Some common applications of in-mold labeling include:
Personal care products such as shampoo bottles, deodorants and soaps
Food packaging including ice cream tubs, yogurt containers, butter tubs and takeaway containers for soups, salads and confectionaries
Cosmetic tubes for sunscreen, lotions and liquid makeup
Household products such as bulk cleaning supplies, laundry detergent and fabric softeners
In recent years, the in-mold labeling market has experienced significant growth, mainly due to the numerous benefits it offers. This trend is expected to continue in the coming years for several reasons.
One major advantage of in-mold labeling is the substantial reduction in labeling costs. Additionally, in-mold labeling products are 100% recyclable, eliminating the need for secondary processes associated with post-molding labeling methods. Another key benefit is the ability of in-mold labeling to produce highly appealing and impressive designs on products. Furthermore, in-mold decoration eliminates the problem of label tampering and ensures higher adhesion.
Brands worldwide have recognized the importance of producing products with high-quality packaging and informative labels. They also seek a labeling method that enhances durability and longevity. In-mold labeling offers the opportunity to create high-quality, clearly instructive, and damage-resistant labels at a reasonable cost. This positions in-mold labeling to make a significant contribution to the labeling markets in the coming years.
The materials used in in-mold labeling make it suitable for a wide range of markets, including food, pharmaceutical, computer, telecommunication, automotive, and personal care products.
The growth of in-mold labeling markets has been particularly notable in the case of light plastic labels and moisture barriers. This can be attributed to the changing purchasing habits of consumers, with more people buying products online. As a result, there is an increased need for products with extended shelf life since online purchases often spend more time in distribution centers before reaching consumers. The demand for products with light plastic film and moisture barriers is expected to rise further in the coming years as the number of online shoppers continues to increase.
In-mold labeling utilizes digital printing technology to print labels, which offers several advantages. Digital printing enables the cost-effective production of lower volume labels. It also allows for variable data printing, making it possible to include codes or numbers on labels in a sequential manner. The ability of digital printing to produce high-quality labels at a lower cost positions in-mold labeling for even greater success in the future.
When using in-mold labeling, there are several design considerations to keep in mind:
Container Shape: Determine whether your container is round, square, or another shape. The shape will impact the layout and placement of the label on the container.
Surface Consistency: Decide whether you want your container to have a smooth or textured surface. This choice will influence the adhesive and label material selection.
Container Appearance: Consider whether you want your container to be clear, glossy, or white. This decision will affect the label material and printing technique used.
Container Requirements: Communicate any specific requirements for your container, such as freezer-grade, autoclave-resistant, or ultra-clear resin. These requirements will guide the selection of materials and processes.
Product Function: Determine the intended function of your product. If it will be exposed to fluctuating temperature environments or harsh conditions, special chemical coatings can be applied to protect the container and ensure durability.
For IML Food Lid:
Container Size: Consider the size of your container. If it is a portion-sized container, such as a 5 oz. jar, the ingredient label may not fit on the body of the container and may need to be placed on the lid or at the bottom.
Label Placement: Be mindful of where you want your label to be printed on the container. Understanding the injection points of the mold can help prevent distortion or interference with the design, avoiding labeling on areas where the injection ends.
In this article, we have delved into the comprehensive details of in-mold labeling, equipping you with a thorough understanding of its benefits, forming process, applications, and market potential, design considerations. We trust that the information presented here will assist you in making informed decisions regarding in-mold labeling, whether for personal or company use.
Navigation
+86 596 6797 686
+86 137 0938 2367
Longchi Development Zone, Jiaomei Town, Taiwanese Investment Zone, Zhangzhou, Fujian, China
